|
In the Film
|
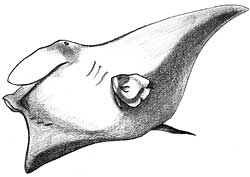
Terns gain protection from predators by living among a colony of gulls. A baby leather bass fish finds protection among sea urchins. Small jack fish swim, unharmed, among the tentacles of the lion's mane jellyfish, while angelfish clean parasites off a manta ray
|
|
Concept
|
Organisms of different species may live together in beneficial relationships.
|
|
Objective
|
To invent two organisms with attributes that allow them to live together as helpful partners
|
|
Content
|
Science, language arts, visual arts
|
|
Background
|
 Within communities, organisms of different species may exist in some form of partnership. These relationships are generally referred to as symbiotic. Mutualism refers to relationships that are beneficial to both organisms. The relationship of flowers and bees is an example of mutualism. A bee moves pollen from one flower to another, thus fertilizing the flowers. At the same time, the bee satisfies its need for food by feeding on nectar produced by the flower. In some relationships, one organism may benefit while the other organism neither gains nor loses. Referred to as commensalism, an example of this type of relationship might be a bird nest in a tree. The bird finds a place to build a nest (benefits), while the tree neither gains nor loses. Parasitism, a third type of relationship, is beneficial to one organism at the expense of another. Fleas on a dog would be an example of parasitism.
Within communities, organisms of different species may exist in some form of partnership. These relationships are generally referred to as symbiotic. Mutualism refers to relationships that are beneficial to both organisms. The relationship of flowers and bees is an example of mutualism. A bee moves pollen from one flower to another, thus fertilizing the flowers. At the same time, the bee satisfies its need for food by feeding on nectar produced by the flower. In some relationships, one organism may benefit while the other organism neither gains nor loses. Referred to as commensalism, an example of this type of relationship might be a bird nest in a tree. The bird finds a place to build a nest (benefits), while the tree neither gains nor loses. Parasitism, a third type of relationship, is beneficial to one organism at the expense of another. Fleas on a dog would be an example of parasitism.
|
|
On the Web
|
The Ocean Oasis Field Guide has pages with photographs and more detailed information about most of the species mentioned here.
|
![[Materials]](images/materials.gif)
Description of organisms, paper, pencil, art supplies
|
![[Procedure]](images/procedure.gif)
(six groups)
- Discuss the types of partnerships that might exist between different organisms in a community—mutualism, commensalism, parasitism.
- Explain that the class will pretend to operate a "dating service" for marine animals. Requests have been received from six animals seeking helpful relationships. Divide the class into six groups. Give each group one of the request sheets.
- Each group designs a poster portraying their client with a list of attributes.
- Display the finished posters.
- Challenge each group to find a partner for their animal that will result in a beneficial relationship for one or both members.
- Describe the relationship between your two partners.
Note: The descriptions are based on real animals seen in the film. However, details have been omitted to encourage creativity. For a list of species appearing in the film visit the Field Guide section of this website.
|

|
|
Dear Marine Matchmakers,
I have enclosed a description of myself. Please help me find a partner.
|
|
1.
Fish
Size: flat, 20 feet across
Color: blackish back, gray underside
Diet: plankton
Motion: slow to fast
Other features: rough skin
Need: removal of parasites
|
2.
Young fish
Size: 6 inches
Color: blue bars on orange body
Diet: algae, parasites
Motion: moderately fast
Other features: lives around reefs
Need: safe place to eat
|
|
3.
Invertebrate
Size: ball-like, 5 inches across, spines up to 10 inches
Color: dark purple
Diet: algae
Motion: slow
Other features: long, slender, toxic spines
Need: nothing special
|
4.
Baby fish
Size: 6 inches
Color: white with dark bars
Diet: small fish, crustaceans
Motion: fast
Other features: lives around reefs, immune to toxins
Need: protection from predators
|
|
5.
Fish
Size: 6 inches
Color: silver
Diet: small fish, small shrimp
Motion: fast, agile swimmer
Other features: immune to toxins, lives around reefs, attracts predators
Need: protection from predators
|
6.
Invertebrate
Size: bowl-shaped, 2 feet across
Color: yellow to red
Diet: small fish, trapped in tentacles
Motion: drifts
Other features: many, very long toxic tentacles
Need: someone to attract food to my tentacles
|
|
|
SUGGESTED PAIRINGS
manta (1) with young angelfish (2) = mutualism
sea urchin (3) with baby leather bass (4) = commensalism
jack (5) with lion's mane jellyfish (6) = mutualism
|
|
Local Connection
Describe some relationships between organisms in your area that exhibit mutualism, commensalism, or parasitism.
Key Words
symbiotic, mutualism, commensalism, parasitism
|
|
Continue to Activity 12: Human Needs and Resources: Comparing Lifestyles
|
![[Ocean Oasis - Teacher's Guide]](images/bnr-oo-tg.gif)

![[Ocean Oasis - Teacher's Guide]](images/bnr-oo-tg.gif)

![[Marine Matchmakers]](images/matchmakers.gif)
![[Materials]](images/materials.gif)
![[Procedure]](images/procedure.gif)
